DISASTER RISK REDUCTION METHODS /FOCUSED ON EDUCATION/
Журнал: Научный журнал «Студенческий форум» выпуск №17(240)
Рубрика: Безопасность жизнедеятельности

Научный журнал «Студенческий форум» выпуск №17(240)
DISASTER RISK REDUCTION METHODS /FOCUSED ON EDUCATION/
Abstract. In the last 5 years, on average, 4660 dangerous incidents and accidents were registered in Mongolia, and 202 people lost their lives due to disasters. For example, only in 2022, 22 percent of people who died in water accidents were children aged 0-17, 85 percent of whom were male and 15 percent female, and 26 percent of people who died in fire were children, 54 percent of whom were male and 46 percent of whom were female. [1]
According to the study, the majority of young children lost their lives due to potential dangers. Although preventive information is regularly disseminated, it is not a good measure to save lives from danger at the right time. Therefore, there is a need for a special prevention method to reduce children’s risk from disasters and accidents. Especially from the examples of developed cities that are regularly hit by disasters, educational institutions place importance on disaster awareness and awareness training.
Keywords: disaster risk reduction methods, disaster, disaster prevention education.
Researched status of the topic: There is a lack of detailed books and research works based on risk assessment in the field of disaster risk reduction in educational institutions throughout Mongolia. Looking at the four research in Mongolia, disaster prevention training was not studied based on risk assessment, but it was studied from the point of view of training of industry experts, training system, disaster prevention training management, management organization, and training methodology.
Research methodology: In 2010, the “One million safe schools” initiative was expanded to provide school safety and disaster education as part of disaster risk reduction activities and the “Safe school” concept has been developing since 2012. In this context, the 3 “safe school” methodology was implemented in a general way using the method based on various interventions in 5 stages.
- Hazard assessment-potential hazard mapping and hazard assessment table
- Vulnerability and capability assessment-non structural vulnerability and capacity assessment
- Disaster risk assessment level-risk assessment matrix and risk reduction strategy
- Disaster risk reduction-determine activities, prioritize, plan and highlight the activities.
- Also, the questionnaire was processed within the framework of the recommendations and plans from the risk assessment.
Research results: The main feature of the modern disaster management concept is the tendency to invest in disaster prevention and disaster risk reduction. Especially, it is aimed at increasing the knowledge and understanding of the people and ensuring the safety of educational institutions.[2]
Table 1.
Comparative study of international experience
|
Only for children |
Bangladesh |
Disaster risk reduction risk mapping for children and maintenance of seasonal calendars are carried out. |
|
Indonesia |
Disaster risk reduction activities are organized in schools across the country to train school-aged children |
|
|
China |
Disaster preparedness training is organized as a special campaign. |
According to the international experience, the understanding of disasters is provided by educational institutions. There is no such educational program in Mongolia. Therefore, in order to determine the needs, 13 state-owned general education schools and 10 non-state-owned schools were selected, and a general disaster risk assessment and survey.
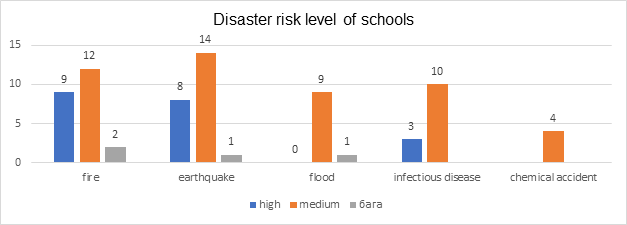
Chart 1. disaster risk level of schools
23 general education schools were considered to be at risk from fire, earthquake, flood, 10 from infectious diseases, and 4 from chemical accidents. 80% of the schools are old buildings from before 2000 or from 1940 to 1989, which can be affected by earthquake and fire.
Each school’s evaluation team members made recommendations and findings to the school administration and senior management to reduce risk.
Table 2
Recommendations from students and teachers in the are of risk reduction
|
№ |
Student |
Teacher and staff |
|
1 |
Inclusion of disaster prevention courses and lessons in the education program |
Improving the standard of school buildings
|
|
2 |
Every child should be able to provide first aid
|
To have a teacher specialized in the field of disasters, to ensure organization |
|
3 |
Capacity building of teachers in the field of disasters
|
Provision of temporary shelters and temporary assembly areas in accordance with standards |
The following issues are urgent in organizing the training:
- Teachers are not trained in disaster management and lack knowledge and understanding.
- If the program is implemented in the education system in the field of disasters, the workload of teachers will increase and the organization of the will be insufficient.
- There are not enough materials and special classrooms for disaster lessons.
- Law and legal regulations are insufficient.
- School buildings do not meet quality standarts and are not durable.
Conclusions and recommendations: When conducting a general disaster risk assessment for educational institutions, it was found that there are about 15 types of dangerous phenomena and accidents in Mongolia, and school buildings are at risk of fire, earthquake, flood, infectious disease, and chemical accident. 80% of the schools are old brick buildings from before 2000 or from 1940 to 1989, which is a risk situation for earthquake and fire. In Mongolia, it is possible to implement programs in general education schools in the field of disasters, and it is considered necessary to include training. If disaster lessons are systematically introduced in the education system, the following importance will generally appear in the future.
- It will be a big step towards achieving the sustainable development goals. /Future personnel will work as a voice in the field of disaster risk.
- By planning for prevention and mitigation activities, damage can be minimized after a disaster. /Economy, life, property, development of the country/
- Vulnerability can be reduced by assessing disaster risk through community participation.
- Depending on the curriculum, school buildings can be built to be disaster-resistant. /The school facility serves as temporary shelter internationally and in Mongolia/
- Gain knowledge and skills to save yourself and others in times of disaster.

